Table of Contents
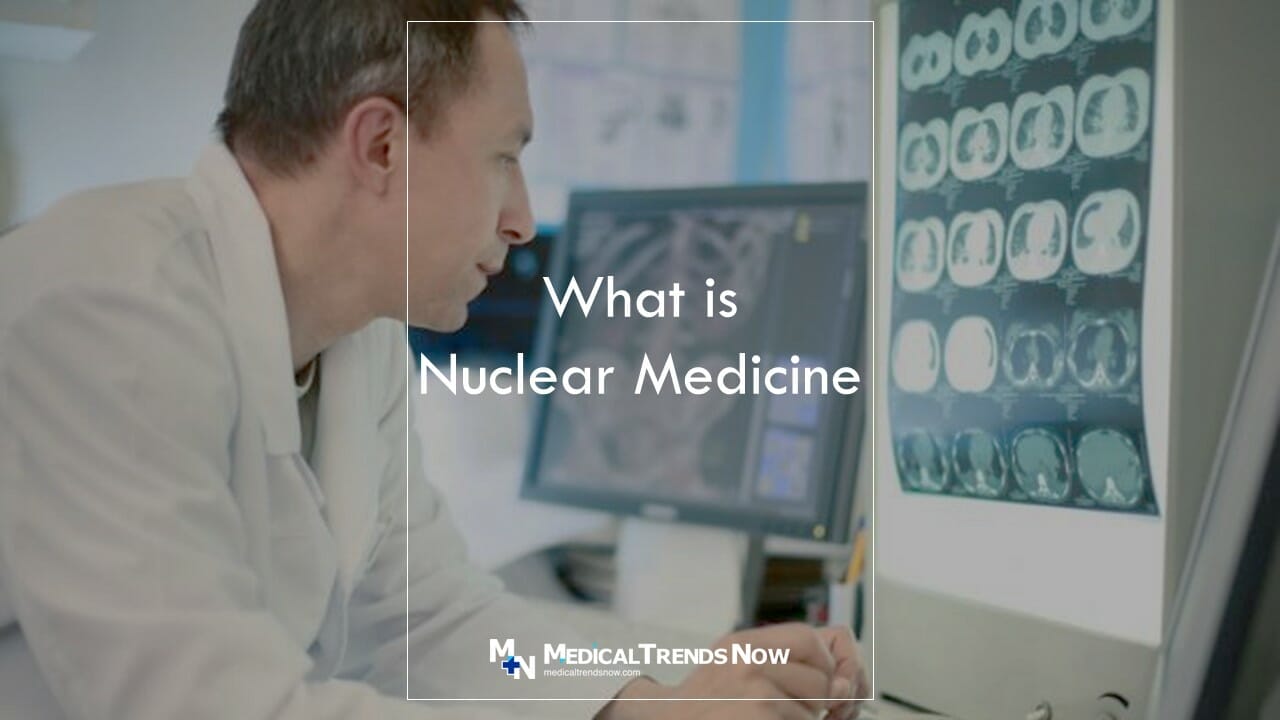
Nuclear Medicine is the most advanced imaging technique! Learn how it works, what is Nuclear Medicine, and how to use it in your practice. Get the ultimate guide for Nuclear Medicine. Keep reading and learn the latest trends in nuclear medicine!
Nuclear medicine is a type of imaging that uses a small amount of radioactive material to produce images. Nuclear imaging is used to diagnose and treat many types of diseases, including cancer.
Nuclear medicine is a specialized field of radiology that uses nuclear imaging to diagnose and treat diseases.
In this article, we will discuss what nuclear medicine is, how it works, and the different types of scans may be performed with nuclear medicine.

What Is Nuclear Medicine?
So what is nuclear medicine? Nuclear medicine is a type of imaging that uses radiation to diagnose and treat diseases. X-rays and other radiologic techniques are used to create images of body organs, tissues, and bones. Common uses for nuclear medicine include the detection of cancer in its early stages, the evaluation of cardiac function, and the assessment of bone health.
How Does Nuclear Medicine Works?
Nuclear medicine uses nuclear radiation as a diagnostic technology tool to collect image body tissues and organs.
Radioactively-labeled ionizing particles are used to create images of the body in real imaging time.
This technology is often used to diagnose and treat diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.

The Different Types Of Tests That Are Performed With Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a branch of radiology that uses radioactive substances to diagnose and monitor diseases. The different tests that are performed with nuclear medicine include:
1. Computerized tomography (CT)
CT scans use a large number of X-rays to create detailed images of organs and tissues in the body. CT scans can be used to look for tumors, cysts, and other abnormalities.
2. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRI scans use powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures. MRI scans can be used to look for tumors, cysts, blood clots, and other abnormalities.
3. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
SPECT scans use a radioactive tracer (small amount of radiotracer) substance that emits only one photon when it is activated by a gamma ray from an atomic nucleus. SPECT scans can show how active certain areas of the brain are in patients with neurological disorders or tumors.
4. Computed tomography with moving object reconstruction (CMR)
CMR scans use multiple CT scans to create a three-dimensional image of the body. CMR scans can be used to look for tumors, cysts, and other abnormalities.
5. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR)
NMR scans use magnetic fields and radio waves to measure the chemical changes that occur in tissue samples. NMR scans can be used to detect Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and other diseases.
Different Types of Nuclear Medicine Tests Applications
There are several different types of nuclear imaging tests that are used to diagnose and monitor diseases:
1. Cardiovascular stress test with nuclear medicine:
This test is used to assess the health of the heart by measuring how well it pumps blood. The test is usually performed after a patient has been diagnosed with hypertension or coronary artery disease.
2. Gallium scan:
This test is used to diagnose various types of cancers, including cervical cancer, thyroid cancer, and leukemia. Gallium scans use a radioactive agent that utilizes injection into the vein or bloodstream and then is detected by a scanner.
3. Bone scan:
This test uses a radioactive agent called fluorine-18 to measure how much calcium is in the bones. The bone scan can be used to detect osteoporosis or other bone diseases.
4. Brain scan:
This test uses a magnetic field and radio waves to image portions of the brain. Brain scans are usually performed on patients who have neurological disorders or tumors.
5. Prolactin level test with nuclear medicine:
This test is used to diagnose breast cancer. Prolactin levels are increased during the early stages of breast cancer, so this test can help identify these tumors early on.

Why Choose Nuclear Medicine Scan Over Other Image Scan Methods?
There are many reasons to choose nuclear medicine over other imaging methods. Nuclear medicine is more sensitive than X-rays and can image smaller objects, such as tumors.
It can also image the body’s interior, which other imaging methods cannot do. Nuclear medicine can be used to diagnose a variety of medical conditions, including cancer and heart disease.
What Are The Risks And Benefits Of Using Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear medicine is a type of imaging that uses radioactive materials to create images of body organs and tissues. It can be used to diagnose diseases or injuries, evaluate the effectiveness of treatment, and monitor patients during treatments.
There are several risks associated with nuclear medicine procedures. These include exposure to radiation, the potential for contamination of the image being taken, and incorrect diagnosis due to the use of inaccurate images. However, nuclear medicine also has some benefits. For example, it can provide detailed images functions of organs and tissues that are difficult to see with other imaging techniques. Additionally, nuclear medicine can be used in conjunction with other treatments to help determine which approach is most effective for a particular patient.

How To Become A Nuclear Medicine Technologist
Nuclear medicine is a medical technology that uses nuclear imaging to diagnose and treat diseases. To become a nuclear medicine technologist, you need to have a degree in biomedical sciences or engineering and two years of experience working as a technician in the field. After completing an accredited nuclear medicine technician program, you will be able to work as an assistant or associate technologist in a hospital or clinic.

Salary of Nuclear Medicine Technologist
Nuclear medicine technologists typically earn a salary in the mid-to high-six figures. It is important to note that salaries vary greatly based on experience and location.
That said, the majority of nuclear medicine technologists work in academic settings, where they may receive excellent benefits and a competitive salary.
Getting Started In Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine is a medical imaging technique that uses radiation to image the body. It is used to diagnose and treat diseases by revealing abnormalities inside the body. Nuclear medicine can be used to image organs, tissues, and bones. It can also be used to image the brain and spinal cord.

How Does Nuclear Medicine Work?
Nuclear medicine is a type of diagnostic imaging that uses radiation to make pictures of the body. Nuclear medicine techniques use radioactive materials, such as radioactive isotopes, to produce images of tissue and organs.
Nuclear medicine can be used to image many parts of the body, including the brain, heart, lungs, liver, and bones. Nuclear medicine images are often very detailed and provide a better understanding of the health of organs and tissues than traditional imaging methods.
Some common nuclear medicine techniques include computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET imaging), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

Which is Better, SPECT or PET in Nuclear Imaging?
Should you go for SPECT or PET? PET scanning is generally considered to be better than SPECT scanning because it can provide more detailed images of the body. SPECT scans use a single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanner to create multiple images that are then analyzed to produce a three-dimensional image.
PET scans use positron-emitting isotopes, which are atoms with an extra neutron in their nucleus, and emit gamma rays when they decay. These rays travel through the body and can be detected by a detector outside the body. PET scans can therefore provide information about the metabolism in different parts of the body, while SPECT scans are better at identifying abnormalities in organs and tissues.

Why Is Nuclear Imaging Needed?
Nuclear medicine is a type of imaging that uses nuclear radiation dose to create pictures. It is used to diagnose and monitor diseases. Nuclear medicine images can help doctors and nuclear medicine personnel see inside the body and detect problems early.
Some of the benefits of nuclear medicine include:
1) It can be used to diagnose a wide variety of diseases, including cancers.
2) It can help doctors see inside the body and detect problems early. This can save lives.
3) It is safe and painless, which makes it a good choice for people who are uncomfortable with other types of imaging procedures.

Who Needs a Radioactive Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear medicine is a type of imaging that uses radioactive materials to create images of body organs and tissues. Nuclear medicine is used to diagnose and treat a wide variety of medical conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
Radioactive nuclear medicine is primarily used by doctors to image the inside of the body. This type of imaging is helpful for diagnosing conditions like cancer, which can be difficult to see with other types of imaging techniques. Radioactive nuclear medicine also helps doctors treat diseases like heart disease and diabetes by identifying problems early on.
Nuclear medicine is an important tool for diagnosing and treating many medical conditions. If you are experiencing any sort of health concern, please feel free to consult with your doctor about whether radioactive nuclear medicine may be right for you.

Where Do Doctors Perform Nuclear Medicine?
Nuclear medicine is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses radioactive material to image the body. Nuclear medicine scans use a variety of radioactive materials, including technetium-99m (Tc-99m), iodine-131, and carbon-14. Doctors may perform nuclear medicine scans in various locations, including the hospital setting, outpatient clinics, and even in the patient’s home.
Nuclear medicine has a wide range of applications for diagnosing diseases and conditions. In particular, nuclear medicine can help diagnose cancerous tumors and assess the effectiveness of treatments. Additionally, nuclear medicine can be used to determine the amount of radiation exposure during radiation therapy or for assessing health risks from exposure to other types of radiation.

How Much Does Nuclear Medicine Cost?
Nuclear medicine is a type of imaging that uses radioactive substances to create pictures of body organs and tissues. This technology is often used to diagnose diseases and to scan for cancerous tumors. The cost of nuclear medicine can vary depending on the procedure and the location where it is performed.
Generally, however, the cost of nuclear medicine scans tends to be higher than other types of common imaging exams. It usually costs about $1,000 to $2,000 per scan.
What is Tracer in Nuclear Medicine?
Tracers are chemicals that are used in nuclear medicine to help physicians diagnose and treat diseases. Tracers are injected into a patient and then tracked using special machines. This allows doctors to see exactly where the tracer is going and what effect it has on the body.
What is Spect in Nuclear Medicine?
Spectroscopy is a type of nuclear medicine that uses photons to identify elements in a body. It is used to diagnose and monitor the health of organs and tissues. Nuclear medicine can help diagnose diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.

What is Positron Emission Tomography in Nuclear Medicine?
Positron emission tomography (PET scanner) is a type of nuclear medicine that uses a radioactive tracer to diagnose diseases in the body.
PET scans use a large number of small radioactive particles to create images of the body. The tracer binds to cancer cells and other tissue abnormalities, which can then be seen on the image. PET scans are used to diagnose cancers such as lung, prostate, and breast cancer; tumors such as brain and liver tumors; and various other diseases.

What is Emission Computed Tomography in Nuclear Medicine?
Emission computed tomography (ECT) is a special type of nuclear medicine scan that can help doctors see inside the body.
ECT uses powerful radiation to create images of the body’s organs and tissues.
What is Single Photon Emission in Nuclear Medicine?
Single Photon Emission in Nuclear Medicine (SPENM) is a diagnostic imaging test technique that uses gamma camera radiation to image the body.
SPENM is used to diagnose various medical conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and stroke.

What are Radioactive Tracers (Radiopharmaceuticals)?
The use of radioactive tracers (also known as radiotracers or also called radiopharmaceuticals) in nuclear medicine has a long and varied history. The earliest tracers were used to help diagnose diseases by tracking the movement of atoms within the body. Today, radioactive tracers are still used to track the movement of atoms within the body, but they can also be used to image organs and tissues.

How Do You choose the Right Nuclear Medicine Physician?
There are a few things that you should consider when choosing a nuclear medicine physician.
First, you should look for a physician who has an extensive background in nuclear medicine.
Second, you should choose a physician who has experience performing nuclear medicine procedures.
Third, you should consider if the insurance covers the healthcare provider, such as imaging agents, myocardial perfusion, and all other imaging tools or imaging devices.
Finally, you should choose a physician who is certified by the American Board of Nuclear Medicine. By taking these steps, you will be able to find the best nuclear medicine physician for your needs.

Conclusion: What is a Nuclear Imaging
A nuclear medicine exam is a powerful diagnostic tool that uses radioactive materials to image the body. By using different types of radiation, nuclear medicine can create images of organs and tissues in the body. Nuclear medicine can help doctors diagnose or treat a patient’s response to treatments for conditions like cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
Nuclear medicine is a valuable diagnostic tool for many conditions.
Becoming a nuclear medicine technologist can be an exciting and challenging career choice. However, it takes dedication and hard work to become successful in this field.
Sources
- Nuclear Medicine Scans for Cancer – American Cancer Society
- Nuclear Medicine – The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists
- Nuclear Medicine: What does a scan involve? – The British Nuclear Medicine Society
- Radiation protection in nuclear medicine – International Atomic Energy Agency
- Nuclear Medicine Imaging – Cleveland Clinic
- Nuclear Medicine – National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB)
- General Nuclear Medicine – Radiological Society of North America
- Radiation in Healthcare: Nuclear Medicine – CDC