Table of Contents
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects women’s ovaries in the Philippines. It can create a number of signs and symptoms, some of which include abnormal menstrual periods, difficulty getting pregnant, and weight gain. There is currently no cure for PCOS, but there are treatments that can help manage the condition.
If you’re concerned that you might have PCOS, this article contains signs and symptoms of what you should watch for and the treatments you may want to consider.
What Is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome PCOS?
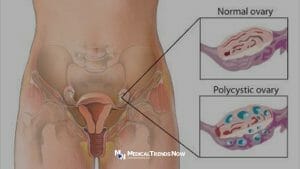
A hormonal problem that occurs during the reproductive years is known as Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). Periods may not occur frequently if you have PCOS. Alternatively, you can get prolonged menstruation. Another possibility for you is that your body contains too much of the hormone androgen
Along the outside edge of the ovary, several tiny fluid sacs form in people with PCOS. These are known as ovarian cysts. Immature eggs are present in tiny cysts filled with fluid. The term for these is follicles. The follicles don’t consistently release eggs.

What PCOS Symptoms that Filipinos Should Watch Out For: Signs and Symptoms of PCOS
PCOS affects many Filipino women. The following are the most common symptoms of PCOS:
1. Irregular Menstrual Periods
This is the most common symptom of PCOS. You may not have a regular period every month, or your periods may be heavier or lighter than usual.
2. Heavy periods
Your periods may be so heavy that you need to take breaks from working out or doing other strenuous activities because you are too tired to continue.
3. Difficulty getting pregnant
If you have difficulty getting pregnant, it is likely that you have PCOS. This difficulty can stem from irregular ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovary) or from low testosterone levels in men.
4. Weight gain
Women with PCOS typically tend to gain weight around their midsection and on their hips and buttocks.
5. Hair loss
Women with PCOS may experience hair loss on the scalp, in the pubic area, or on the chest.
6. Skin problems
Women with PCOS may have a higher incidence of skin problems, such as acne, oily skin, and excessive dryness.
7. Acne
Women with PCOS are more likely to have severe acne than women without PCOS.
8. Insomnia
About one-third of women with PCOS report difficulty sleeping at some point during their lives.
If you have any of the signs and symptoms listed above, your Filipino gynecology doctor may consider diagnosing you with PCOS.
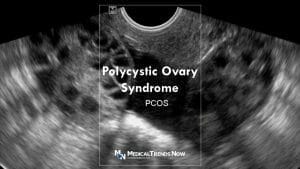
What Causes PCOS?
Some factors that may play a role in polycystic ovary syndrome. Filipina patients with PCOS have the following features:
1. Genetics
PCOS is thought to be caused by a combination of genes and environmental factors.

2. Insulin resistance
Filipino women with polycystic ovarian syndrome often have insulin resistance, which means their body doesn’t effectively use insulin. This can lead to problems with ovulation and the menstrual cycle, as well as type 2 diabetes.
Your body may produce an excessive amount of the male hormone androgen levels if you take in too much insulin. The process by which eggs are released from the ovary, known as ovulation, may be difficult for you.
Dark, velvety patches of skin under the breasts, in the groin, armpits, or lower region of the neck are indications of insulin resistance. Other symptoms could include an increase in appetite and weight.
3. Obesity
Women with PCOS are more likely to be obese than women without the condition. Obesity can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance and other health problems related to polycystic ovary syndrome.
4. Sedentary lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle can also increase your risk of developing PCOS because it leads to a decrease in testosterone and hormone levels.

Possible Effects of PCOS
Infertility
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome are also more likely to experience difficulty becoming pregnant. This may be due to problems with ovulation or problems with the lining of the uterus (the endometrium).
Increased risk of miscarriage or Premature delivery
Women with the polycystic ovarian syndrome are at a higher risk of miscarriage, especially early in pregnancy
Heart disease
Women with PCOS are at a higher risk of heart disease, especially if they have obesity or diabetes.
Joint pain
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome may experience joint pain, which can be due to the overall condition or to specific symptoms, such as acne.
Difficulty concentrating
Women with the polycystic ovarian syndrome may have difficulty concentrating, especially when trying to focus on tasks that require mental effort.
Mood swings
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome may experience mood swings, which can be due to the overall condition or to specific symptoms, such as acne.
PCOS may also cause infertility. The cause of infertility associated with PCOS is negligence. If left untreated, many women with PCOS may not be impregnated.
Other Complications of PCOS include:
- Metabolic syndrome: a collection of disorders that considerably raise your risk of heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) illness, such as high blood pressure, excessive blood sugar, and bad cholesterol or triglyceride levels.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a severe liver inflammatory condition brought on by the liver fat accumulation
- Gestational diabetes or pregnancy-induced high blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Sleep apnea
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Eating Disorders
- Cancer of the uterine lining (endometrial cancer)
What are the Tests? How is PCOS Diagnosed
Your symptoms, medications, and any additional medical issues will probably be discussed at first with your healthcare professional in the Philippines. Your Filipino doctor can also inquire about your menstrual cycles and any weight fluctuations. A physical examination includes looking for indications of excessive hair growth, insulin resistance, and acne.
The following tests may be recommended to diagnose PCOS:
1. Ultrasound
Your ovaries’ condition and the thickness of your uterus’ lining can both be diagnosed with PCOS via ultrasound examination. Your vagina receives a transducer, which resembles a wand. Sound waves released by the transducer are converted into visuals on a computer screen.
2. Pelvic Exam
Your healthcare professional might examine your reproductive organs during a pelvic exam to look for lumps, growths, or other changes. This is part of the diagnosis of PCOS.
3. Blood Exams/Work-up
Hormone levels can be determined via blood tests. This testing can rule out other reasons for irregular menstruation or androgen excess that resemble PCOS.
Other blood tests, such as ones to check your triglyceride and cholesterol levels after a fast, may be performed on you. You can measure how your body reacts to sugar with a glucose tolerance test (glucose).
Other Tests may include:
- Regular assessments of cholesterol and triglyceride levels, glucose tolerance, and blood pressure
- Depression and anxiety testing
- Obstructive sleep apnea screening
How is PCOS Treated: Possible Treatments for PCOS
To treat PCOS, the management of polycystic ovary syndrome starts with the management of your worries. Try not to overthink, and do not stress yourself. Your PCOS condition might evolve into obesity, hirsutism, acne, or infertility if not managed properly.
Medication or lifestyle modifications may be part of a specific treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Medications for PCOS
The following medications may be recommended by your health practitioner:
1. To aid the regulation of periods
Combination of Birth Control Pills
Estrogen and progestin-containing pills reduce androgen production and control estrogen. By balancing your hormones, you can reduce your chance of endometrial cancer and get rid of acne, unwanted hair growth, and irregular bleeding.

Progestin Therapy
Your cycles can be controlled, and endometrial cancer can be avoided by taking progestin for 10 to 14 days every one to two months. This won’t stop pregnancy and doesn’t raise testosterone levels.
2. To aid ovulation
Clomiphene
During the first phase of your menstrual cycle, you may take this oral anti-estrogen drug. Clomiphene is a medication that is typically used to treat fertility issues in women. It is a non-hormonal medication that works by tricking the body into believing that there is less estrogen in the body than there actually is. This then causes the pituitary gland to release more follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which can stimulate ovulation.

The ovaries may be stimulated by this breast cancer medication. Letrozole is a medication that has been used to treat breast cancer. Recently, however, letrozole has been shown to be an effective treatment for ovulation disorders. This medication works by inhibiting the production of estrogen in the body. By doing so, letrozole can help to induce ovulation in women who have difficulty ovulating on their own.

This oral type 2 diabetes medication enhances insulin resistance and reduces insulin levels. Your doctor in the Philippines may advise adding metformin to assist you to ovulate if you are on clomiphene and are unable to become pregnant. Metformin can help you lose body weight and delay the onset of type 2 diabetes if you have prediabetes.
Metformin is a medication typically used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is also used to prevent the onset of diabetes in Filipinos with prediabetes. Metformin works by reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and increasing the sensitivity of cells to insulin. The result is lower blood sugar levels. Metformin is usually taken orally, either as a tablet or an extended-release tablet.

Gonadotropins
These are given by injecting these hormones. Gonadotropins are a class of hormones that bind to and activate gonadotropin receptors. They are named for their role in the regulation of the gonads, where they stimulate the production of sex hormones. The gonadotropins are follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). In females, FSH stimulates the growth and development of ovarian follicles, while LH triggers ovulation and the production of progesterone.
3. To aid in reducing excessive hair growth and acne
Birth Control Pills
These pills limit the production of androgen, which can lead to acne and excessive hair growth.
There are many benefits to birth control pills, one of which is reducing excessive hair growth and acne. This is a great option for women who are looking for a way to control their hormones and reduce the amount of unwanted hair. Birth control pills work by regulating the hormones in your body, which can help to reduce the production of testosterone. This can lead to a decrease in hair growth, as well as fewer breakouts. If you are considering this method of contraception, be sure to speak with your doctor in the Philippines about which option is best for you.
The effects of androgen on the skin, such as increased hair growth and acne, are blocked by this medicine. While using this drug, effective birth control is required because spironolactone might lead to birth abnormalities. If you are pregnant or intend to become pregnant, you shouldn’t use this drug.
Spironolactone is a medication that has been used to treat various conditions, including heart failure, hypertension, and edema. In recent years, spironolactone has been shown to be effective in treating acne and hirsutism in women. Acne is a common skin condition that affects thousands of Filipinos. The cause of acne is thought to be related to hormones. Spironolactone is a medication that can help to reduce the amount of testosterone in the body, which can help to reduce acne breakouts. Hirsutism is a condition characterized by excessive hair growth on the face, chest, and back. Hirsutism can be caused by an excess of testosterone in the body.

Eflornithine slows facial hair growth. Eflornithine, also known as Vaniqa, is a medication used to treat excessive hair growth. It is a topical cream that is applied to the skin. Eflornithine works by inhibiting the production of enzymes that are necessary for hair growth. Eflornithine is most effective when used in conjunction with other hair removal methods, such as shaving, waxing, or electrolysis. It is important to note that eflornithine will not permanently remove hair. However, it can help to reduce the amount of hair that grows back after these other methods are used. If you are considering using eflornithine to reduce excessive hair growth, be sure to speak with your Filipino doctor first. This medication is not right for everyone, and it is important to make sure that it is safe for you to use.

Hair Removal
There are two methods for getting rid of hair: electrolysis and laser hair removal. A focused light beam is used during the medical treatment of laser hair removal to remove unwanted hair. You might require a number of electrolysis or laser hair removal sessions. Other treatments include shaving, hair removal by plucking, or lotions that destroy unwanted hair. These are only temporary, and as the hair regrows, it could become thicker.

Acne Treatments
The condition of acne may be improved by drugs, including oral pills and topical creams or gels. Options should be discussed with your healthcare provider.

Home Remedies to Address PCOS:
The following tips can be done to help reduce and ease the effects of PCOS:
Limit Carbohydrate and Calorie Intake
Consuming a lot of carbohydrates may raise your insulin levels. If you have polycystic ovarian disease, inquire with your Filipino doctor if a low-carb diet would be beneficial. Pick complex carbs over simple ones since they will cause your blood sugar levels to rise less quickly. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, cooked dry beans and peas, and legumes are all sources of complex carbohydrates.
Maintain a Healthy Weight.
Insulin and testosterone levels can drop with weight loss. Additionally, it might make ovulation happen again. If you think you might need one, talk to your doctor in the Philippines about a weight-control program. Consult a trained dietician for assistance in achieving your weight-loss objectives.
Be Active.
Blood sugar levels can be reduced through exercise. Increased daily activity and consistent exercise may be used to treat or even prevent insulin resistance in PCOS patients in the Philippines. Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding diabetes may both benefit from being active.
Conclusion: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
If you have PCOS, it’s important to understand the signs and symptoms, as well as the causes. Following a healthy lifestyle may help reduce your risk of complications like infertility and obesity. If you’re struggling to manage your PCOS, talk to your Filipino doctor about the best ways to treat it.
Resources: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- Features of PCOS: POLYCYSTIC OVARIES: A COMMON FEATURE IN TRANSVAGINAL SCANS OF GYNAECOLOGICAL PATIENTS – National Library of Medicine
- Women with polycystic ovarian syndrome: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – Johns Hopkins Medicine
- The Androgen Excess and PCOS Society criteria for the polycystic ovary syndrome: the complete task force report – AE-PCOS Society report on PCOS phenotype
- Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome – NHS
- Common causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – Cleveland Clinic
- Exact cause of PCOS in ovary – Causes: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. – NHS
- Assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome: summary of an evidence-based guideline – National Library of Medicine
- Obese women with PCOS – Obesity and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome – PMC – NCBI
- Evaluation and Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome – NCBI
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome – American Academy of Family Physicians AAFP
- Diagnosis of Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) – Mayo Clinic
- PCOS have a hormonal imbalance – Polycystic ovary syndrome – Office on Women’s Health
- Diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome in adults – UpToDate
- Treatment of Hirsutism – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic
- Treatment of pcos to get pregnant – Treatments for Infertility Resulting from PCOS | NICHD
- PCOS have insulin resistance – Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Diabetes | CDC
- Infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome – The management of anovulatory infertility in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: an analysis of the evidence to support the development of global WHO guidance – Oxford University Press, University of Oxford
- Anovulation in PCOS – Review What causes anovulation in polycystic ovary syndrome? – Science Direct
- (Ovarian Diathermy) Laparoscopic Ovarian Drilling for PCOS – My Health Alberta
Disclaimer: Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
This website is intended to educate both members of the general public and those working in the medical field on the prevalence, causes, and methods for preventing, diagnosing, and treating diseases that affect people throughout their lives. This website’s content is provided solely for informational reasons and is not meant to serve as a substitute for the advice of a qualified medical practitioner.